1. Install Microsoft Cluster Server.
2. Create and name a cluster resource group.
3. Create a new IP address resource.
4. Create a new network name resource.
5. Move the disk to the cluster resource group.
6. Test the cluster.
7. Install Microsoft Exchange Server on the primary node.
8. Install Microsoft Exchange Server on the secondary node.
NoteIf you want to upgrade an existing Microsoft Exchange Server installation and install it into an existing cluster, you can move all users from the existing Microsoft Exchange Server computer to a new clustered Microsoft Exchange Server computer. For more information, see “Migrating an Existing Microsoft Exchange Server Computer into a Cluster” later in this document.
Monday, February 21, 2011
Implementing Exchange Server in a Cluster Environment
Typical scenarios:
Installing a new Exchange Server computer into a cluster.
Moving users from an existing Exchange Server computer to a new Exchange Server computer in a cluster.
Migrating an existing Exchange Server computer to a cluster.
Guidelines:
Exchange Server must be installed into an operational cluster. It is not possible to install Cluster Server onto an existing Exchange Server installation.
Nodes in the cluster must have these common attributes:
Memory, local hard drive, and processor configurations must be identical because Exchange Server assumes symmetrical performance of both nodes of the cluster.
Before installing Exchange Server, you must create a cluster resource group for use by Exchange Server clustered resources.
Installing a new Exchange Server computer into a cluster.
Moving users from an existing Exchange Server computer to a new Exchange Server computer in a cluster.
Migrating an existing Exchange Server computer to a cluster.
Guidelines:
Exchange Server must be installed into an operational cluster. It is not possible to install Cluster Server onto an existing Exchange Server installation.
Nodes in the cluster must have these common attributes:
Memory, local hard drive, and processor configurations must be identical because Exchange Server assumes symmetrical performance of both nodes of the cluster.
Before installing Exchange Server, you must create a cluster resource group for use by Exchange Server clustered resources.
How Clusters Work
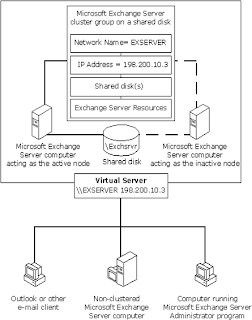
A cluster consists of two Exchange Server computers (called nodes) that share:
one or more common physical disk drives
an IP address
a network name
and Exchange Server cluster resources
Within a Microsoft Exchange Server cluster, only one of the nodes in the cluster can service network requests at any one time.
The node that owns all clustered resources is called the active node. It owns the shared disk(s), the IP address, and the network name for the cluster, and it runs the Microsoft Exchange Server services. If the active node in a cluster experiences a hardware failure, Microsoft Exchange Server services fail over to the inactive node, which then becomes the active node.
Exchange Cluster -3
Dependencies
Many clustered resources are dependent on other resources for operation. Setup creates the dependencies for all resources except the Microsoft Mail Connector.
Physical disk resource
The disk resource shared between servers in a cluster. The physical disk hosts Microsoft Exchange Server-related files and databases and is a member of the Microsoft Exchange Server cluster group.
Exchange Server resources
Many Microsoft Exchange Server resources can exist within the Microsoft Exchange Server cluster group. Because Microsoft Exchange Server is cluster aware, these services are automatically created and configured during Setup and configuration of Microsoft Exchange Server into the cluster.
Many clustered resources are dependent on other resources for operation. Setup creates the dependencies for all resources except the Microsoft Mail Connector.
Physical disk resource
The disk resource shared between servers in a cluster. The physical disk hosts Microsoft Exchange Server-related files and databases and is a member of the Microsoft Exchange Server cluster group.
Exchange Server resources
Many Microsoft Exchange Server resources can exist within the Microsoft Exchange Server cluster group. Because Microsoft Exchange Server is cluster aware, these services are automatically created and configured during Setup and configuration of Microsoft Exchange Server into the cluster.
Exchange Cluster - 2
Virtual server
The network interface presented to the network on behalf of the Microsoft Exchange Server cluster group. A virtual server is a combination of the network name and the IP address resources. All requests to the Microsoft Exchange Server cluster are directed to the virtual server.
Active node
The cluster server that currently owns cluster group resources and responds to network requests made to those services. In a Microsoft Exchange Server cluster environment, only one of the clustered nodes can be active at a given time.
Inactive node
The cluster server that does not currently own cluster group resources but is available if the active node fails over.
Exchange cluster resource group
A logical grouping of Microsoft Exchange Server cluster resources for the purpose of administration and fail over.
The network interface presented to the network on behalf of the Microsoft Exchange Server cluster group. A virtual server is a combination of the network name and the IP address resources. All requests to the Microsoft Exchange Server cluster are directed to the virtual server.
Active node
The cluster server that currently owns cluster group resources and responds to network requests made to those services. In a Microsoft Exchange Server cluster environment, only one of the clustered nodes can be active at a given time.
Inactive node
The cluster server that does not currently own cluster group resources but is available if the active node fails over.
Exchange cluster resource group
A logical grouping of Microsoft Exchange Server cluster resources for the purpose of administration and fail over.
Understanding_Cluster
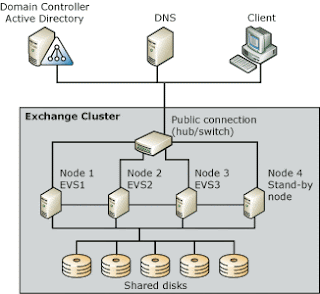
Primary node
The cluster server on which the Microsoft Exchange Server is initially installed.
Secondary node
The other server in a cluster server. The secondary node copies information from the primary node during installation and supplemental updates.
Network name resource
The network name of the cluster virtual server. This is the network name accessed by clients connecting to the cluster. This name must be unique within the network.
IP address resource
A static IP address associated with the virtual server’s network name. This is the IP address accessed by clients connecting to the cluster. The IP address must be unique within the network.
Saturday, February 19, 2011
Count Janus Hassildor

Yes, three, count em’, three mitten n glove patterns, and three times as many colourways, all inspired by Buffy The Vampire Slayer, an’ featuring some of our fave quotes from our fave characters!!
The Midnight Collection package is 3 skeins of indigodragonfly MCN yarn (1 MCN Worsted, 1 MCN Sock and either an MCN Sport or 2nd skein of MCN Sock), accompanied by three new patterns from the lovely & talented Glenna C, and all this can be yours for a special discounted price of $93!
Thursday, February 17, 2011
Exchange 2003 Troubleshooting - 16 GB Limt
Exchange Server Mailbox Store does not mount when the Mailbox Store database reaches the 16-GB limit
Event Type: Error Event Source: MSExchangeIS Event Category: General Event ID: 1112
Event Type: Warning Event Source: ESE Event Category: Space Management Event ID: 445
We can temporarily increase the Exchange 2000 16-gigabyte database size limit.
The Microsoft Exchange 2000 Server message database (MDB) automatically shuts down and does not restart when it reaches the maximum size limit that is permitted. This behavior is by design to prevent the database from trying to insert more data into the database file than it was designed to hold. Frequently, you experience this behavior when you are running Microsoft Exchange 2000 Server Standard Edition. Exchange 2000 Server Standard Edition limits the database size to 16 gigabytes.
Temporarily increase the database size limit by 1 GB.
•Selectively remove unnecessary database content.
•Defragment the database to reduce the database to a level that is in the defined boundaries of the database size.
Prerequisites:>
Because of file dependencies, this update requires Microsoft Exchange 2000 Server Service Pack 3 (SP3). For more information, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base: 301378
Create New Registry Value
The update requires you to create a new registry value to enable this feature.
To add the registry entry to the Exchange 2000 computer, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Run, and then type regedt32.exe.
Locate the following key in the registry: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchangeIS\\Private- GUID.
On the Edit menu, click Add Value, and then type the following in the Value name box: Temporary DB Size Limit Extension
Select REG_DWORD for the data type, and then click OK
Enter a value of 1, and then click OK
Quit Registry Editor
However, this registry value is not read dynamically; it is only read when a database is started. When the Exchange Information Store starts, an event 9657 will be logged as a warning to inform you that you are using a temporary database size limit.
To prevent new e-mail content from being added to the mailbox store beyond the temporary 17-GB limit during the recovery process, Microsoft strongly recommends that you stop the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) service and the Microsoft Exchange MTA Stacks service (if it is running) before you mount the mailbox store
Mount your mailbox store
Remove data from your mailbox store. To do this, use any of these methods:>
Use Microsoft Outlook to delete unnecessary e-mail items from individual inboxes and other folders.
Use Outlook to delete unnecessary e-mail items from the Sent Items folder
Use Outlook to empty the Deleted Items folder.
If deleted item retention is set, you may want to temporarily reduce retention to zero (0) days:
a. Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft Exchange, and then click System Manager
b. Right-click Mailbox Store, and then click Properties
c. Click the Limits tab, and then type 0 in the Keep deleted items for days box.
Delete mailboxes that are no longer used.
Use the Move Mailbox tool to move mailboxes to a mailbox store that is on another Exchange server
Go to the basics again:>
Have users create personal folder (.pst) files on their local hard drives and then archive content from the mailbox store database to their local hard drives.
Open Exchange System Manager. To do this, click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft Exchange, and then click System Manager.
Double-click the Exchange server, and then double-click Storage Group
Right -click Mailbox Store, and then click Properties
Lets to advance things
Click the Database tab, and then click Customize to modify the schedule to run immediately. Online maintenance may take up to 30 minutes to start and several hours to complete. When online maintenance has started, the following event ID message is logged in the application event log:
Event Type: Information Event Source: ESE Event Category: Online Defragmentation Event ID: 700 Description: MSExchangeIS (170) Online Defragmentation is beginning a full pass on database 'C:\exchsrvr\mdbdata\priv1.edb'.
View the application event log to verify that online maintenance of your mailbox store is complete. Event ID1221 indicates that online maintenance is complete. This event ID message also indicates how much free space there will be on your mailbox store after offline defragmentation. Event ID 1221 appears similar to the following message: Event Type: Information Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store Event Category: General Event ID: 1221 Description: The database Storage Group Name\Mailbox Store has 565 megabytes of free space after online defragmentation has terminated.
Run an offline defragmentation of your mailbox store by using the Eseutil tool (Eseutil.exe). You must dismount the mailbox store before you run an offline defragmentation, and you must have free disk space equal to at least 110% of the database size to run eseutil /d drivefrom where you are running this command.
Apply Service Pack 2 on the E2K3.
.SP2 is available from the following link:
http://www.microsoft.com/exchange/downloads/2003/sp2/default.mspx
Registry Key for Configurable DB size limit:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchangeIS\\Private-
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Name: Database Size Limit in GB
Value:
Standard: 1 - 75
Enterprise: 1 - 8000
Database Size Buffer Warning
Upon mounting the store, we compare the physical database size against the Configured Database Limit.
If the physical size is within or exceeds the configured “Database Size Warning Buffer” then the store will do a logical calculation of the database size.
If the physical size is below the configured “Database Size Warning Buffer” then there is no need to calculate the fee space because logical size will always be <= physical size
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchangeIS\\Private-
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Name: Database Size Buffer in Percentage
Value: 1-100
Timing of the Database Size Check
By default, timing of the database size check will occur at 5A.M. and run off 24-hr intervals
Both time and interval are configured via registry per database
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchangeIS\\Private-
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Name: Database Size Check Start Time in Hours From Midnight
Value: 1 – 24
Lets Go through the Troubleshooting Of the SP2:
Event IDs 1216/1217 are logged when mounting the database. Event ID 1216 is logged on Standard SKU or if configurable database size limit has been set on Enterprise SKU. Event ID 1217 is logged on Enterprise SKU only.
Event Type: Information
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 1216
Computer: Name
Description: The Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)' is limited to 1 GB. The current physical size of this database (the .edb file and the .stm file) is 1 GB. If the physical size of this database minus its logical free space exceeds the limit of 1 GB, the database will be dismounted on a regular basis
Event Type: Information
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 1217
Computer: Name
Description: The Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)' has unlimited storage capacity. The current physical size of this database (the .edb file and the .stm file) is 1 GB. The only size constraint for this database is the maximum size that is supported by the database storage engine (8000 GB).
Event ID 9685 is logged at database mount and Physical size increases:
Event Type=Warning
Information store '%1': The physical database size (physical size of the EDB file and the STM file) is %2 Gb, which has exceeded the maximum size limit of %3 Gb for this database. However, the logical free space in the database has not yet been evaluated, so it is possible that there is ample free space in the database to bring its logical size below the maximum size limit.
%n%nIf the logical database size exceeds this limit, it will be forced to dismount on a regular basis
Event ID 9686 is logged at database mount and whenever the database size check start time is changed. (requires logging levels to be set to MINIMUM
Event Type: Information
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 9686
Computer: Name
Description: Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)': A check of the logical size of this database (the logical size equals the physical size of the .edb file and the .stm file minus the logical free space in each) is scheduled to be performed on a regular basis.
Size Limit: 1 GB
Warning Threshold: 10 %
Initial Size Check: 5AM
Size Check Interval: 1 minutes
Event ID 9687 is logged when the database size check task is
executed. (requires logging levels to be set to MINIMUM)
Event Type: Information
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 9687
Computer:Name
Description: Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)': A check of the logical size of this database (the logical size equals the physical size of the .edb file and the .stm file minus the logical free space in each) will now be performed.
Size Limit: 1 GB
Warning Threshold: 10 %
Initial Size Check: 5AM
Size Check Interval: 1 minutes
Event ID 9688 is logged when the database size check task is executed logged whenever the size check task is executed and the logical database size exceeds the warning threshold but not the maximum size.
EventID=9688
Event Type=Warning
Information store '%1': The logical database size (physical size of the EDB file and the STM file minus the logical free space in each) is %2 Gb, which is approaching the size limit of %3 Gb for this database.
%n%nIf the logical database size exceeds this limit, it will be forced to dismount on a regular basis
Event ID 9689 is logged whenever the database size check task
is executed and the logical database size exceeds the maximum
size, but the database will not be dismounted. This will give an
administrator until the next size check task execution to correct
the situation
Event Type: Error
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 9689
Computer: Name
Description: Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)': The logical size of this database (the logical size equals the physical size of the .edb file and the .stm file minus the logical free space in each) is 1 GB. This database size has exceeded the size limit of 1 GB
Event Type: Error Event Source: MSExchangeIS Event Category: General Event ID: 1112
Event Type: Warning Event Source: ESE Event Category: Space Management Event ID: 445
We can temporarily increase the Exchange 2000 16-gigabyte database size limit.
The Microsoft Exchange 2000 Server message database (MDB) automatically shuts down and does not restart when it reaches the maximum size limit that is permitted. This behavior is by design to prevent the database from trying to insert more data into the database file than it was designed to hold. Frequently, you experience this behavior when you are running Microsoft Exchange 2000 Server Standard Edition. Exchange 2000 Server Standard Edition limits the database size to 16 gigabytes.
Temporarily increase the database size limit by 1 GB.
•Selectively remove unnecessary database content.
•Defragment the database to reduce the database to a level that is in the defined boundaries of the database size.
Prerequisites:>
Because of file dependencies, this update requires Microsoft Exchange 2000 Server Service Pack 3 (SP3). For more information, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base: 301378
Create New Registry Value
The update requires you to create a new registry value to enable this feature.
To add the registry entry to the Exchange 2000 computer, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Run, and then type regedt32.exe.
Locate the following key in the registry: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchangeIS\
On the Edit menu, click Add Value, and then type the following in the Value name box: Temporary DB Size Limit Extension
Select REG_DWORD for the data type, and then click OK
Enter a value of 1, and then click OK
Quit Registry Editor
However, this registry value is not read dynamically; it is only read when a database is started. When the Exchange Information Store starts, an event 9657 will be logged as a warning to inform you that you are using a temporary database size limit.
To prevent new e-mail content from being added to the mailbox store beyond the temporary 17-GB limit during the recovery process, Microsoft strongly recommends that you stop the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) service and the Microsoft Exchange MTA Stacks service (if it is running) before you mount the mailbox store
Mount your mailbox store
Remove data from your mailbox store. To do this, use any of these methods:>
Use Microsoft Outlook to delete unnecessary e-mail items from individual inboxes and other folders.
Use Outlook to delete unnecessary e-mail items from the Sent Items folder
Use Outlook to empty the Deleted Items folder.
If deleted item retention is set, you may want to temporarily reduce retention to zero (0) days:
a. Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft Exchange, and then click System Manager
b. Right-click Mailbox Store, and then click Properties
c. Click the Limits tab, and then type 0 in the Keep deleted items for days box.
Delete mailboxes that are no longer used.
Use the Move Mailbox tool to move mailboxes to a mailbox store that is on another Exchange server
Go to the basics again:>
Have users create personal folder (.pst) files on their local hard drives and then archive content from the mailbox store database to their local hard drives.
Open Exchange System Manager. To do this, click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft Exchange, and then click System Manager.
Double-click the Exchange server, and then double-click Storage Group
Right -click Mailbox Store, and then click Properties
Lets to advance things
Click the Database tab, and then click Customize to modify the schedule to run immediately. Online maintenance may take up to 30 minutes to start and several hours to complete. When online maintenance has started, the following event ID message is logged in the application event log:
Event Type: Information Event Source: ESE Event Category: Online Defragmentation Event ID: 700 Description: MSExchangeIS (170) Online Defragmentation is beginning a full pass on database 'C:\exchsrvr\mdbdata\priv1.edb'.
View the application event log to verify that online maintenance of your mailbox store is complete. Event ID1221 indicates that online maintenance is complete. This event ID message also indicates how much free space there will be on your mailbox store after offline defragmentation. Event ID 1221 appears similar to the following message: Event Type: Information Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store Event Category: General Event ID: 1221 Description: The database Storage Group Name\Mailbox Store has 565 megabytes of free space after online defragmentation has terminated.
Run an offline defragmentation of your mailbox store by using the Eseutil tool (Eseutil.exe). You must dismount the mailbox store before you run an offline defragmentation, and you must have free disk space equal to at least 110% of the database size to run eseutil /d drivefrom where you are running this command.
Apply Service Pack 2 on the E2K3.
.SP2 is available from the following link:
http://www.microsoft.com/exchange/downloads/2003/sp2/default.mspx
Registry Key for Configurable DB size limit:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchangeIS\
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Name: Database Size Limit in GB
Value:
Standard: 1 - 75
Enterprise: 1 - 8000
Database Size Buffer Warning
Upon mounting the store, we compare the physical database size against the Configured Database Limit.
If the physical size is within or exceeds the configured “Database Size Warning Buffer” then the store will do a logical calculation of the database size.
If the physical size is below the configured “Database Size Warning Buffer” then there is no need to calculate the fee space because logical size will always be <= physical size
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchangeIS\
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Name: Database Size Buffer in Percentage
Value: 1-100
Timing of the Database Size Check
By default, timing of the database size check will occur at 5A.M. and run off 24-hr intervals
Both time and interval are configured via registry per database
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchangeIS\
Data Type: REG_DWORD
Name: Database Size Check Start Time in Hours From Midnight
Value: 1 – 24
Lets Go through the Troubleshooting Of the SP2:
Event IDs 1216/1217 are logged when mounting the database. Event ID 1216 is logged on Standard SKU or if configurable database size limit has been set on Enterprise SKU. Event ID 1217 is logged on Enterprise SKU only.
Event Type: Information
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 1216
Computer: Name
Description: The Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)' is limited to 1 GB. The current physical size of this database (the .edb file and the .stm file) is 1 GB. If the physical size of this database minus its logical free space exceeds the limit of 1 GB, the database will be dismounted on a regular basis
Event Type: Information
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 1217
Computer: Name
Description: The Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)' has unlimited storage capacity. The current physical size of this database (the .edb file and the .stm file) is 1 GB. The only size constraint for this database is the maximum size that is supported by the database storage engine (8000 GB).
Event ID 9685 is logged at database mount and Physical size increases:
Event Type=Warning
Information store '%1': The physical database size (physical size of the EDB file and the STM file) is %2 Gb, which has exceeded the maximum size limit of %3 Gb for this database. However, the logical free space in the database has not yet been evaluated, so it is possible that there is ample free space in the database to bring its logical size below the maximum size limit.
%n%nIf the logical database size exceeds this limit, it will be forced to dismount on a regular basis
Event ID 9686 is logged at database mount and whenever the database size check start time is changed. (requires logging levels to be set to MINIMUM
Event Type: Information
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 9686
Computer: Name
Description: Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)': A check of the logical size of this database (the logical size equals the physical size of the .edb file and the .stm file minus the logical free space in each) is scheduled to be performed on a regular basis.
Size Limit: 1 GB
Warning Threshold: 10 %
Initial Size Check: 5AM
Size Check Interval: 1 minutes
Event ID 9687 is logged when the database size check task is
executed. (requires logging levels to be set to MINIMUM)
Event Type: Information
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 9687
Computer:Name
Description: Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)': A check of the logical size of this database (the logical size equals the physical size of the .edb file and the .stm file minus the logical free space in each) will now be performed.
Size Limit: 1 GB
Warning Threshold: 10 %
Initial Size Check: 5AM
Size Check Interval: 1 minutes
Event ID 9688 is logged when the database size check task is executed logged whenever the size check task is executed and the logical database size exceeds the warning threshold but not the maximum size.
EventID=9688
Event Type=Warning
Information store '%1': The logical database size (physical size of the EDB file and the STM file minus the logical free space in each) is %2 Gb, which is approaching the size limit of %3 Gb for this database.
%n%nIf the logical database size exceeds this limit, it will be forced to dismount on a regular basis
Event ID 9689 is logged whenever the database size check task
is executed and the logical database size exceeds the maximum
size, but the database will not be dismounted. This will give an
administrator until the next size check task execution to correct
the situation
Event Type: Error
Event Source: MSExchangeIS Mailbox Store
Event ID: 9689
Computer: Name
Description: Exchange store 'First Storage Group\Mailbox Store (Name)': The logical size of this database (the logical size equals the physical size of the .edb file and the .stm file minus the logical free space in each) is 1 GB. This database size has exceeded the size limit of 1 GB
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)